Fibromyalgia is a medical condition characterized by widespread pain and fatigue. Although no cure is available, treatment can help reduce the severity of symptoms and improve the health-related quality of life.
This article covers:
- Treatments for fibromyalgia
- What are the medicines used to treat fibromyalgia?
- What are the non-pharmacological therapies for fibromyalgia?
- What are the alternative treatments for fibromyalgia?
- Lifestyle changes that can help alleviate the symptoms of fibromyalgia
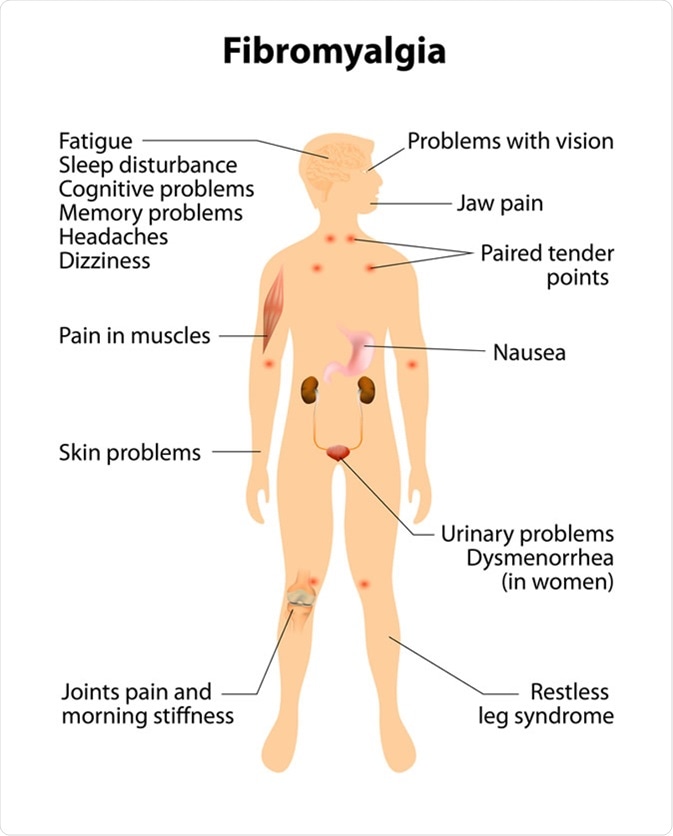
Treatments for fibromyalgia
Since fibromyalgia is not associated with any particular injury or damage to the tissues of the body, it is often very difficult to find the right treatment. As fibromyalgia symptoms are both physical and psychological, a patient may need help from different healthcare professionals to effectively manage the condition.
For example, a rheumatologist who treats medical conditions related to muscles and joints may be required to treat the pain-related symptoms of a fibromyalgia patient. Similarly, a neurologist who is specialized for nervous system-related problems can help a patient overcome neurological symptoms, such as sleep disturbance, fatigue, and cognitive and memory problems. Most importantly, given the significant impact of fibromyalgia on emotional behavior, a psychologist (specialized for mental health and psychological treatments) plays an important role for improving overall quality of life of a fibromyalgia patient.
Treatment for fibromyalgia varies from person to person, and patients often require a combination of treatments for proper symptom management. Because of the wide range of symptoms, a patient generally goes through a variety of treatment options to find the right combination. Fibromyalgia treatments frequently include a combination of medicines, non-pharmacological therapies, and lifestyle changes. Alternative treatments including acupuncture, massage, aromatherapy, etc. are also effective.
What are the medicines used to treat fibromyalgia?
Regarding pharmacological treatments, a physician must keep a proper balance between the drug efficacy and adverse side-effects. A time-to-time monitoring of drug dose and treatment duration is also important to avoid unnecessary adversity and drug dependency.
Medicines that are commonly used to treat fibromyalgia patients are as follows:
Pain killers – most frequently used over-the-counter pain killers are acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen or naproxen. Although not very effective in alleviating fibromyalgia-related pain, these drugs are helpful in treating pain triggers of fibromyalgia. For this reason, these drugs mostly benefit patients who have other pain-causing disorders, such as arthritis, in addition to fibromyalgia.
Other mild pain killers, such as paracetamol, may be effective for some patients, but may not be helpful for everybody.
Narcotic pain killers are not recommended for fibromyalgia patients as they induce drug dependency and do not address underlying factors that may serve as triggers.
Anti-depressants – are also effective in reducing pain in some fibromyalgia patients. These medicines include tricyclic anti-depressants (amitriptyline), serotonin-noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors (duloxetine and venlafaxine), and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (fluoxetine and paroxetine).
Another drug of choice for fibromyalgia is pregabalin. This antiepileptic medicine is the first drug approved by FDA for treating fibromyalgia patients. Another drug of same category is Gabapentin. Pregabalin differs from other approved anti-depressants in terms of mode of action. It works by blocking α2δ calcium channels and inhibiting the release of excitatory neurotransmitters from presynaptic vesicles. Clinical studies have indicated that treatment with pregabalin reduces pain sensation and improves sleep and health-related quality of life in fibromyalgia patients. However, treatment with this drug should be cautiously monitored because of adverse side-effects, such as dizziness, sleepiness, cognitive dysfunction, swelling, and weight gain.
Sodium oxybate is a sodium salt of gamma-hydroxybutyrate (a short-chain fatty acid), which is a neurotransmitter synthesized from its precursor gamma amino butyric acid (GABA). Sodium oxybate is approved by FDA for the treatment of narcolepsy. It mainly acts by binding to GABA-B receptors. Several randomized, controlled clinical trials have shown that this drug is effective in reducing pain and fatigue and improving sleep quality (increased slow-wave sleep duration and decreased night-time awakenings). Adverse side-effects reported by these studies are headache, nausea, dizziness, and sleepiness. However, so far, FDA did not approve this drug for treating fibromyalgia patients because of drug addiction concerns.
Sleep-promoting medicines – medicines that are used to reduce pain are also useful for improving sleep quality in fibromyalgia patients. These medicines include cyclobenzaprine, amitriptyline, gabapentin, and pregabalin. Sleep-promoting agents like zolpidem or benzodiazepine are not recommended for fibromyalgia patients.
What are the non-pharmacological therapies for fibromyalgia?
Some non-pharmacological interventions can be very effective for fibromyalgia patients in terms of managing symptom intensities and improving the efficacy of pharmacological treatments.
Physical therapy – is the most effective treatment for fibromyalgia. Studies have shown that a regular bout of exercise, especially aerobic exercise, helps reduce the pain and stiffness and improve the strength, body flexibility and posture, and stamina. A patient may take advice from a physiotherapist on how to perform physical activity safely and effectively while in pain.
Walking or water-based exercises are also equally important to begin with. One should start with low-intensity, short-duration exercise and gradually increase it depending on the body’s capacity.
Other physical therapies, such as yoga and Tai Chi, which include both exercise and relaxation, are particularly helpful in improving disrupted sleep and overall quality life. Tai Chi is a mind-body exercise that includes meditation, deep breathing, and relaxation. Studies in a small group of fibromyalgia patients have shown that regular practice of Tai Chi helps reduce fibromyalgia symptoms, including pain, sleep disturbance, depression, and anxiety.
Occupational therapy – helps manage the day-to-day activities without elevating the pain intensity. Occupational therapists mainly use specific locomotion approaches to adjust or overcome work-related symptoms. They also demonstrate how to use labor-saving devices to reduce pain and fatigue at workplace.
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) – is a type of talk therapy that focuses on the emotional aspects of the pain. Pain is not only a physical experience but also an important trigger for emotional distress, including mood swing, fear, frustration, anxiety, and depression. Emotional responses to pain can significantly affect the behavior of a person. CBT primarily aims at separating these different phases of pain experience to better manage each symptom distinctly. In each CBT session, a trained counselor teaches the patient about skills and techniques to deal with painful situations and fight negative thoughts.
What are the alternative treatments for fibromyalgia?
Several complementary or alternative therapies are effective in temporarily reducing the fibromyalgia symptoms. However, clinical studies in this area are scanty to prove the long-term efficacy of these therapies.
Despite not having enough scientific evidence, these alternative therapies are popular as they are safe and without adverse side-effects. Following is the list of alternative therapies that may benefit fibromyalgia patients.
Acupuncture – is a traditional Chinese therapy that aims at restoring normal balance to different energies in the body. The method includes inserting fine needles into specific points in the body that help altering the blood flow and neurotransmitter level in the brain and spinal cord. Studies have found that compared to no treatment or standard therapy, acupuncture helps reduce the pain and stiffness in fibromyalgia patients.
Massage therapy – is one of the oldest techniques used to relieve fibromyalgia pain. Studies have shown that massage therapy has modest, short-term benefits for fibromyalgia symptoms. The method involves manual manipulation of body’s soft tissues, including muscles, connective tissues, ligaments, and tendons. Massage therapy is particularly useful for reducing heart rate, improving joint movement, relaxing muscle, and increasing the release of endogenous pain relieving compounds. It also helps reduce stress and anxiety.
Aromatherapy – this method utilizes essential oils extracted from plants. The oil is mainly used for massage or inhalation purposes, which ultimately helps reduce long-lasting fibromyalgia pain, stress, and anxiety.
Hydrotherapy/balneotherapy – hydrotherapy involves special types of exercises that are performed in a warm-water pool (water temperature: 33 – 36°C). Balneotherapy is a type of hydrotherapy that involves bathing in mineral springs to treat diseases. Studies have shown that balneotherapy temporarily improves pain and quality of life in fibromyalgia patients.
Alternative medicines – some fibromyalgia patients get benefits from using alternative medicines. Till date, three types of medicines have been studied clinically. These include capsaicin (reduces the level of a pain transmitter called Substance P), SAMe or S-adenosylmethionine (an endogenous compound that stimulates cartilage production), and anthocyanidins (an antioxidant that prevent the degradation of collagen). In randomized clinical trials, all these compounds have shown only low-to-moderate level of efficacy in treating fibromyalgia symptoms.
Lifestyle changes that can help alleviate the symptoms of fibromyalgia
Some self-care tips that are vital for the management of fibromyalgia symptoms are as follows:
Regular physical activity – being physically active (walking, swimming, biking, water aerobics, or stretching exercises) for 150 minutes a week can effectively reduce fibromyalgia symptoms. The exercises may increase the pain initially; however, a patient is often benefited from regular practice and gradual increment of exercise load.
Good sleep habit – getting enough sleep is essential for fibromyalgia patients to reduce fatigue. A good sleep habit can be achieved by getting sufficient sleep time, maintaining proper schedule for going to bed and getting up in the morning, and limiting daytime naps.
Stress reduction – fibromyalgia patients should get sufficient relaxation between their day-to-day activities. This is important for limiting overexertion and emotional stress.
Pacing – it is important for fibromyalgia patients to work within their limits to avoid unnecessary pain and fatigue. One should not work too much on a good day or too little on a bad day to achieve a healthy balance.
Healthy lifestyle – eating healthy and balanced diet and limiting the consumption of caffeine helps improve fibromyalgia symptoms.
Sources
- Versusarthritis.org. Fibromyalgia. (2018). www.versusarthritis.org/about-arthritis/conditions/fibromyalgia/
- Rheumatology.org. Fibromyalgia. (2019). www.rheumatology.org/…/Fibromyalgia
- Bupa.co.uk. Fibromyalgia. (2019). www.bupa.co.uk/health-information/brain-nervous-system/fibromyalgia
- Nccih.nih.gov. 6 Things to Know About Mind and Body Practices for Fibromyalgia. (2017). https://nccih.nih.gov/health/tips/fibromyalgia
- Staud R. (2011). Sodium oxybate for the treatment of fibromyalgia. Expert Opin Pharmacother. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21679091
- Boomershine CS. (2010). Pregabalin for the management of fibromyalgia syndrome. J Pain Res. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3004647/
Further Reading
- All Fibromyalgia Content
- What is Fibromyalgia?
- Fibromyalgia Explained
- What Causes Fibromyalgia?
- Fibromyalgia in Children
Last Updated: Jun 10, 2019

Written by
Dr. Sanchari Sinha Dutta
Dr. Sanchari Sinha Dutta is a science communicator who believes in spreading the power of science in every corner of the world. She has a Bachelor of Science (B.Sc.) degree and a Master's of Science (M.Sc.) in biology and human physiology. Following her Master's degree, Sanchari went on to study a Ph.D. in human physiology. She has authored more than 10 original research articles, all of which have been published in world renowned international journals.
Source: Read Full Article
