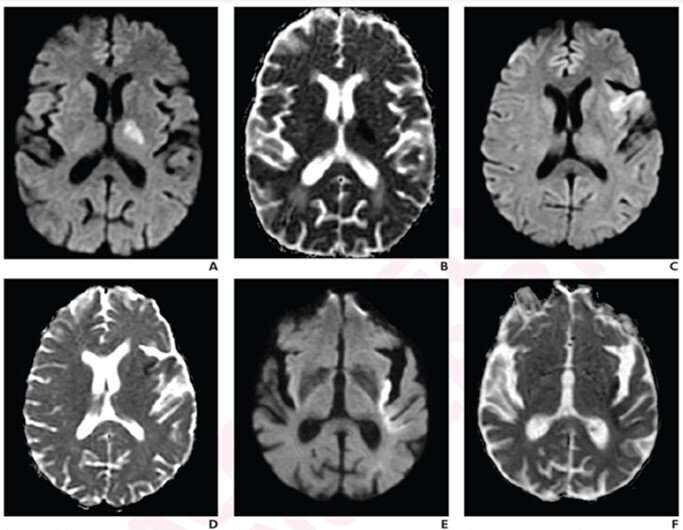
According to a study published American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), percent insular ribbon infarction (PIRI) complements current stroke outcome predictors, classifying patients with slowly progressive stroke who could benefit from late-window endovascular thrombectomy (EVT).
Noting that PIRI was independently associated with infarct growth rate and 90-day outcome, “PIRI may help identify patients who could benefit from late-window EVT when requiring transfer to EVT-capable centers,” wrote head researcher Robert W. Regenhardt, MD, Ph.D., from the department of neurology at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School.
Analyzing a previous clinical trial of acute stroke patients untreated with reperfusion therapies from January 2007 to June 2009, Regenhardt et al. reevaluated 31 trial patients (median age, 71 years; 12 female, 19 male) with anterior-circulation large-vessel occlusion who underwent serial MRI examinations.
Two neuroradiologists independently scored PIRI on presentation MRI—mild (0-1), moderate (2), severe (3-4)—based upon length ratios of the insula portion showing restricted diffusion to the insula’s total length. A 90-day modified Rankin Scale (mRS) was also obtained.
Ultimately, in multivariable models controlling for age, large-vessel occlusion location, and collateral pattern, PIRI category was a significant independent predictor of presentation-to-48-hour infarct growth rate (β=1.3) and 90-day mRS ≤2 (OR=0.2). Sensitivity and specificity for predicting 90-day mRS ≤2 were 90% and 84% for mild-to-moderate PIRI, versus 70% and 74% for symmetric collateral pattern.
“To our knowledge,” the authors of this AJR accepted manuscript added, “the present study is the first to show the PIRI category to be an independent predictor of 90-day mRS <2 in multivariable models."
More information:
Robert W. Regenhardt et al, Percent Insular Ribbon Infarction for Predicting Infarct Growth Rate and 90-Day Outcomes in Large-Vessel Occlusive Stroke: Secondary Analysis of Prospective Clinical Trial Data, American Journal of Roentgenology (2023). DOI: 10.2214/AJR.22.28852
Journal information:
American Journal of Roentgenology
Source: Read Full Article
