Hyperhidrosis is the term used to describe excessive sweating. Usually, the sweat-producing glands secrete sweat in response to a raised body temperature. The sweat cools on the skin and lowers body temperature.
This may occur in response to a number of factors that overheat the body such as a hot environment or exercise. In hyperhidrosis, this sweat production does not necessarily occur in response to such factors and the body sweats even though the body does not require cooling.
Hyperhidrosis is a common condition that may affect the whole body or a particular part of the body such as the armpits, face, chest, groin, palms, or soles of the feet. In most cases, both sides of the body are affected, so sweat glands in both of the feet or both of the armpits, for example, will produce the sweat in excess.
Treatments
Although the condition does not pose any serious health threat, it can interfere with a person’s usual daily activities, as well as causing distress and anxiety. In many cases, people with this condition are too embarrassed to seek medical attention or they believe that there are no treatments available.
However, individuals with this condition should visit their doctor, as researchers are continually improving treatments and many effective treatments are available. Some of these treatments are described in more detail below. In most cases, less invasive treatments are recommended first.
Lifestyle changes
Although making lifestyle changes cannot cure a person’s hyperhidrosis, it can help to improve symptoms and make the person feel more comfortable and confident. Examples of lifestyle measures that can be taken include the following:
- Avoiding behaviors that seem to trigger the problem such as eating spicy food or drinking alcohol
- Frequently using antiperspirants, as opposed to deodorant
- Using armpit shields that absorb excess sweat
- Avoiding wearing restrictive, tight and uncomfortable clothing
- Wearing socks that absorb sweat and avoiding socks comprised of man-made materials
- Changing socks at least twice a day and wearing different pairs of shoes every day.
Medications
Antiperspirant
If the use of a regular antiperspirant is not sufficient to control a patient’s hyperhidrosis, a stronger antiperspirant containing aluminium chloride may be prescribed. This is usually applied to the affected areas before going to bed and is then washed off in the morning.
The product can irritate the eyes and skin. Patients should avoid getting any in their eyes and if the skin becomes irritated, a hydrocortisone cream may be prescribed.
Antidepressants
Certain drugs that are used to treat depression, also have the effect of reducing sweating. Furthermore, they may help decrease sweating in people whos condition is triggered by anxiety.
Nerve-blocking drugs
Certain drugs work by blocking the chemicals that enable communication between certain nerves. For some people, this can decrease sweating, although potential side effects include blurred vision, dry mouth, and bladder problems.
Botox injections
Botulinum toxin injections can block communication between nerves and sweat glands. Patients receive several injections in each affected body part. The effects can last for us long as 6 to 12 months, after which further injections are required.
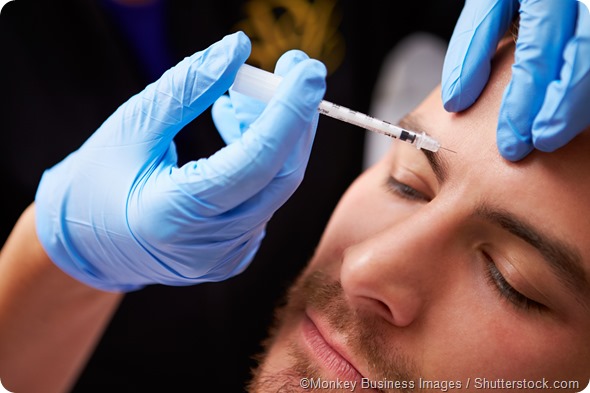
Surgery
Iontophoresis
Here, a device is applied that delivers a weak electric current to affected areas through water or a wet pad, to help block sweat glands. If the hands or feet are being treated, they are placed in water, through which the current is passed. For the underarms, the current is passed through a wet contact pad that is placed under each armpit.
Patients usually need to be treated twice daily over a course of three to four weeks, with each session lasting between 20 and 30 minutes. This can lead to a reduction in sweating after one or two weeks, after which repeat treatment is required at one to four week intervals, depending on symptom severity. This treatment cannot be used for patients who are pregnant or who have a pacemaker.
Removal of the sweat glands
If the sweating is isolated to just the underarms, removing the sweat glands located there may relieve sweating. Several techniques are used to achieve this, which include:
- Making very small incisions in the skin to access the glands and remove them through liposuction or curettage (scraping)
- Holding a probe above the skin that emits electromagnetic radiation to break down the sweat glands
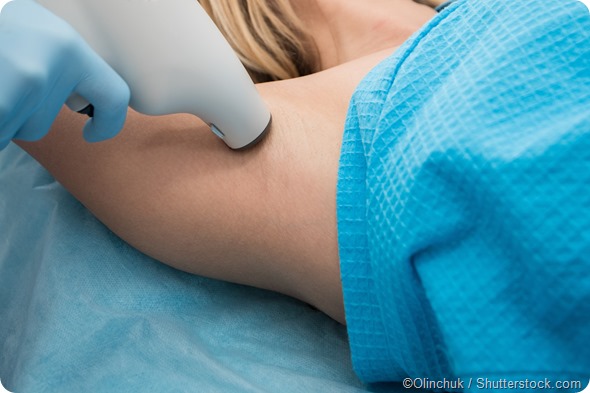
- Making a small incision in the skin, through which a laser is passed and used to destroy the glands
Nerve surgery
If a patient has severe hyperhidrosis in the hands that fails to respond to other treatments, nerve surgery may be recommended. The spinal nerves that trigger sweating in the hands are severed, burned, or clamped. However, sometimes the use of this technique results in excessive sweating in other body areas.
Sources
- http://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Hyperhidrosis/Pages/Treatment.aspx
- www.mayoclinic.org/…/con-20030728
- www.mayoclinic.org/…/con-20030728
- www.aad.org/public/diseases/dry-sweaty-skin/hyperhidrosis#treatment
- http://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Hyperhidrosis/Pages/Introduction.aspx
- http://my.clevelandclinic.org/services/heart/disorders/hyperhidrosis
Further Reading
- All Hyperhidrosis Content
- Hyperhidrosis Causes
- Hyperhidrosis Prognosis and Epidemiology
- Hyperhidrosis Symptoms
- Hyperhidrosis – Excessive Sweating
Last Updated: Feb 26, 2019

Written by
Sally Robertson
Sally has a Bachelor's Degree in Biomedical Sciences (B.Sc.). She is a specialist in reviewing and summarising the latest findings across all areas of medicine covered in major, high-impact, world-leading international medical journals, international press conferences and bulletins from governmental agencies and regulatory bodies. At News-Medical, Sally generates daily news features, life science articles and interview coverage.
Source: Read Full Article
